Abstract
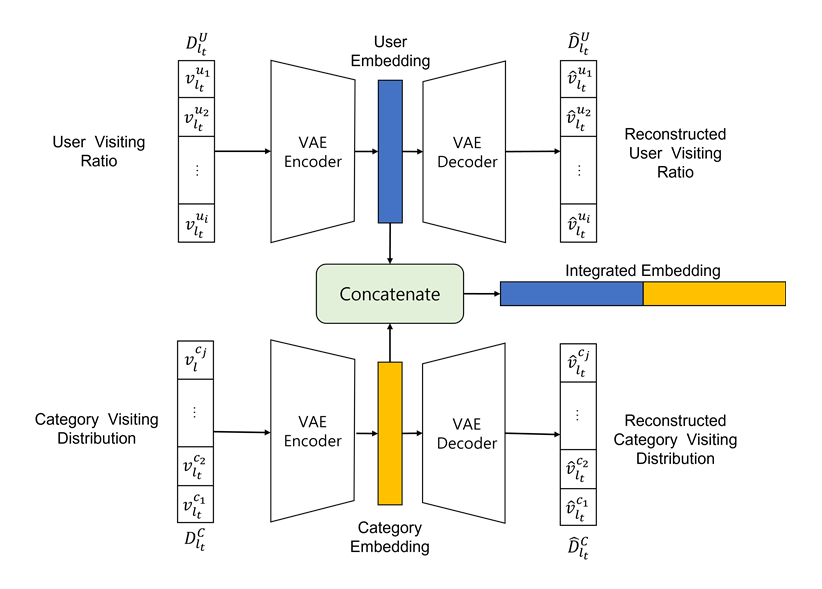
Location-Based1 Social Networks (LBSNs) are social networking services that allow users to share the Points of Interest (POIs) they have visited. The data from LBSNs are used for personalized place recommendations and the analysis of user mobility. In this study, we propose a method to analyze LBSN data from two perspectives: the functionalities provided by different areas in a city and the mobility of users visiting those areas. Specifically, we employ the Variational Auto Encoder (VAE) to embed the distribution of user visits over POI categories and the distribution of user visits over areas for each area. We then use these embeddings to analyze the similarity of areas. The analysis reveals that user visits are concentrated in relatively nearby areas, while areas with similar functionalities are distributed widely across the entire city. Furthermore, we found that user visits have a stronger influence than the visited categories in determining the characteristics of areas.